
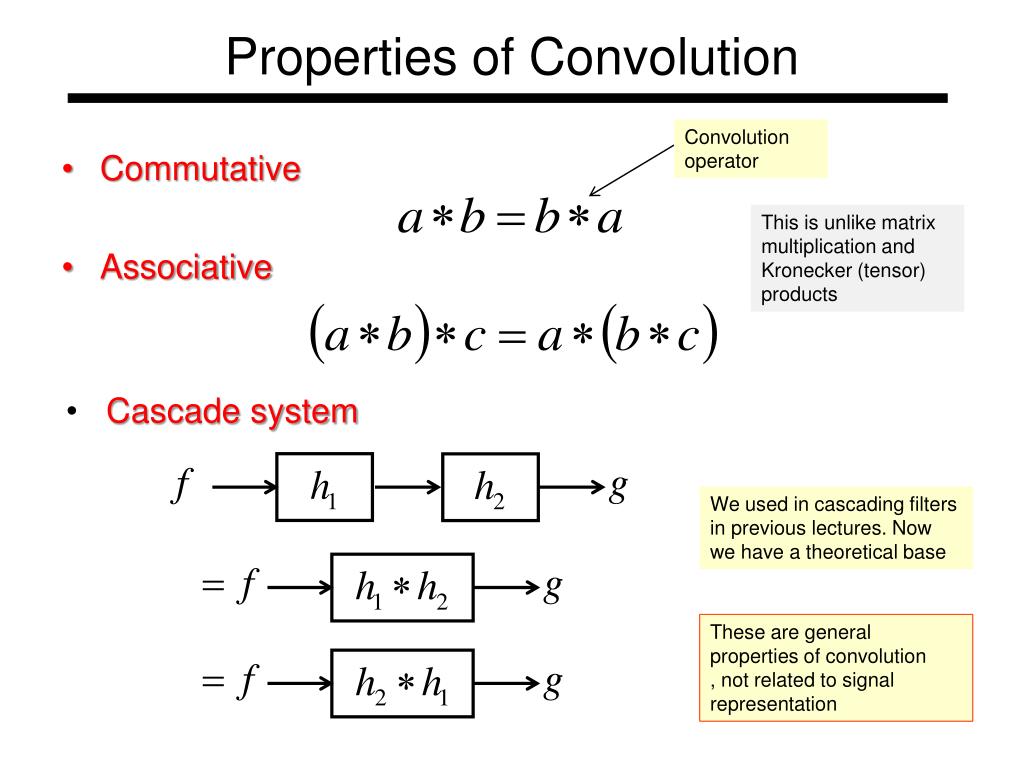
Here flipping of a kernel means flipping values across all axes. Draelos in her article 17, convolution means sliding a flipped kernel h across a signal f, while cross-correlation means sliding a kernel h across a signal f. Convolution versus Cross-CorrelationĬonvolution and cross-correlation are similar operations with slight differences. Note that in the white paper integration is used for all continuous use cases and for discrete use cases, summation is used. Convolution for 1D and 2D signals is described in detail in later sections in this white paper. In image processing, convolution provides a way of multiplying together two arrays of numbers of the same dimensions 4 (for example 1D or 2D) however, they can be of different sizes (for example 3x4 convolved with 20x30). Where f is the input signal, h can be referred as a kernel, t is time, tau is the shift in time, and the asterisk symbol is usually used to represent convolution.
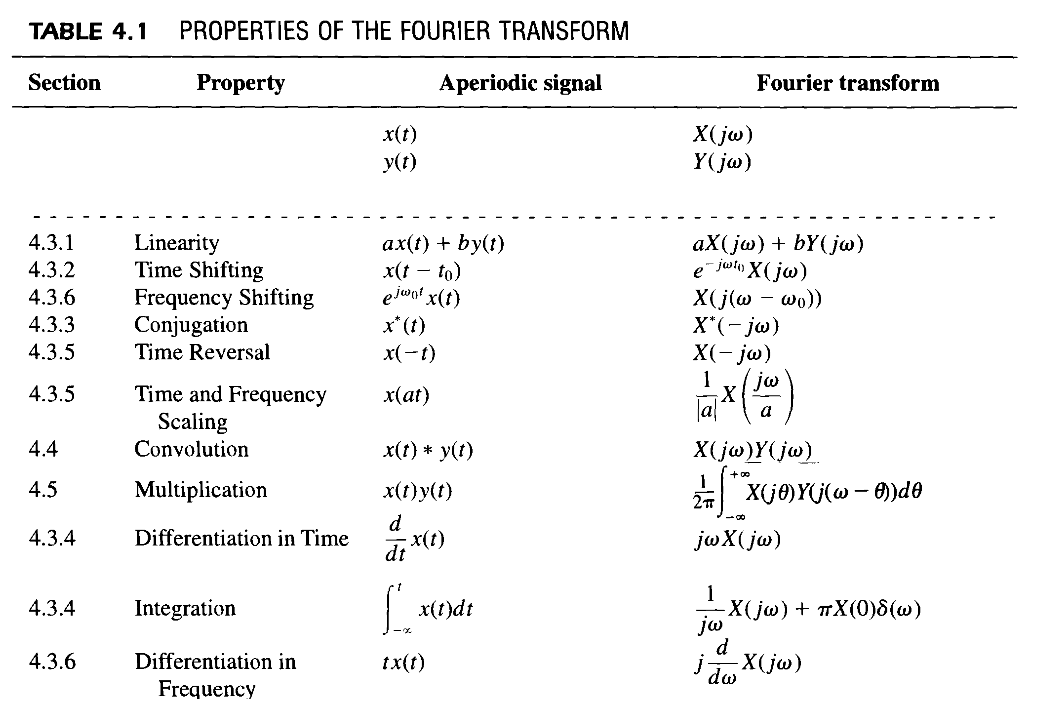
A continuous case convolution of two functions f and h can be mathematically represented the time domain as follows. Hlavac 1 describes convolution as an integral mixing of two functions where one function is overlaid and shifted over another. ConvolutionĬonvolution is a mathematical operation that is fundamental to various image-processing activities. This paper is for a beginner technical audience and provides a glimpse of FFT and convolution in the medical imaging domain. However, similar concepts could apply to other modalities and respective image reconstruction procedures. Here, medical imaging has been confined to computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET).
This white paper provides an overview of fast Fourier transform (FFT), convolution, their application in medical image reconstruction, and gives example code showcasing the use.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
